August 10 NEC Energy News
¶ “Community Solar: Panels Without A Roof” • As the cost of solar decreases each year, all forms of solar are within reach of more people. One form, community solar, is growing especially fast. According to the National Renewable Energy Lab, capacity has grown by 121% year-over-year since 2010. That trend that is expected to continue. [CleanTechnica]
¶ “Solar Leads 16.8 GW US Grid Addition In First Half Of 2023” • The EIA released a report on the power grid’s growth and usage for the first half of 2023. Solar power led with 35% of all new installations, natural gas had 34% (there were also retirements), wind stood was 19%. Batteries took 11%. One nuclear reactor was installed seven years late. [Environment+Energy Leader]
¶ “World’s Largest Lithium Mine Is In Australia” • Not long ago, people were discussing the scarcity of lithium. Now, most of the world’s lithium comes from Australia, which has bountiful reserves of hard rock spodumene. The world’s largest hard-rock lithium mine is the Pilbara Minerals’ Pilgangoora Mine, in Western Australia. [CleanTechnica]
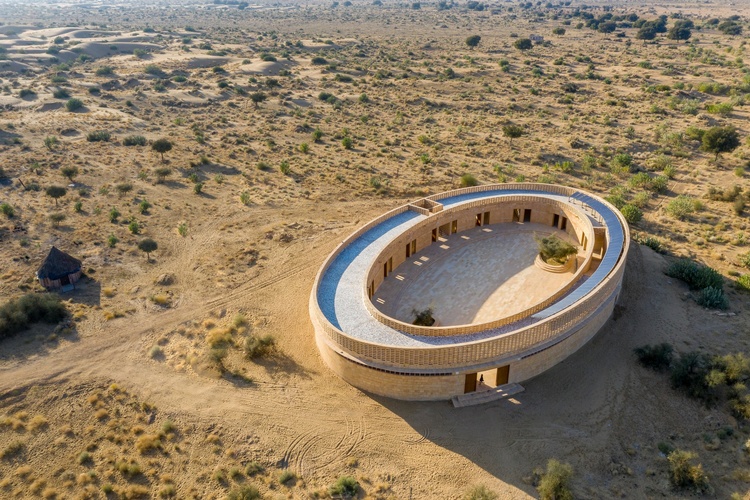
¶ “How This School In The Indian Desert Stays Cool Even In Extreme Heat” • In the north Indian desert town of Jaisalmer, temperatures can reach approximately 120°F (49°C) at the height of summer. Here, buildings have long been designed to adapt to the heat. New York architect Diana Kellogg used that tradition for the Rajkumari Ratnavati Girls’ School. [CNN]

¶ “Extreme Heat Will Make Grand Canyon Visits Dramatically More Risky In The Future, Study Says” • Extreme heat fueled by climate change will significantly increase the risk of heat-related illness for the people who visit Grand Canyon National Park each year, a National Park Service study found. The increase could be 137% by 2100, in a worst case scenario. [CNN]
¶ “Texas Power Use Hits Another Record During Heat Wave” • Demand for power in Texas hit a record high on Wednesday for the second time this week and ninth time this summer as homes and businesses used air conditioners to escape a lingering heat wave. Energy analysts point out that wind and solar power have helped ERCOT meet record demand. [SaltWire]
For more news, please visit geoharvey – Daily News about Energy and Climate Change.
